Infertility Awareness Event

What is infertility?
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse (six months if the woman is over 35 years old). Infertility affects both men and women and can be caused by a variety of factors.
Usually, it is advised to see an infertility specialist sooner if you have one of these risk factors:
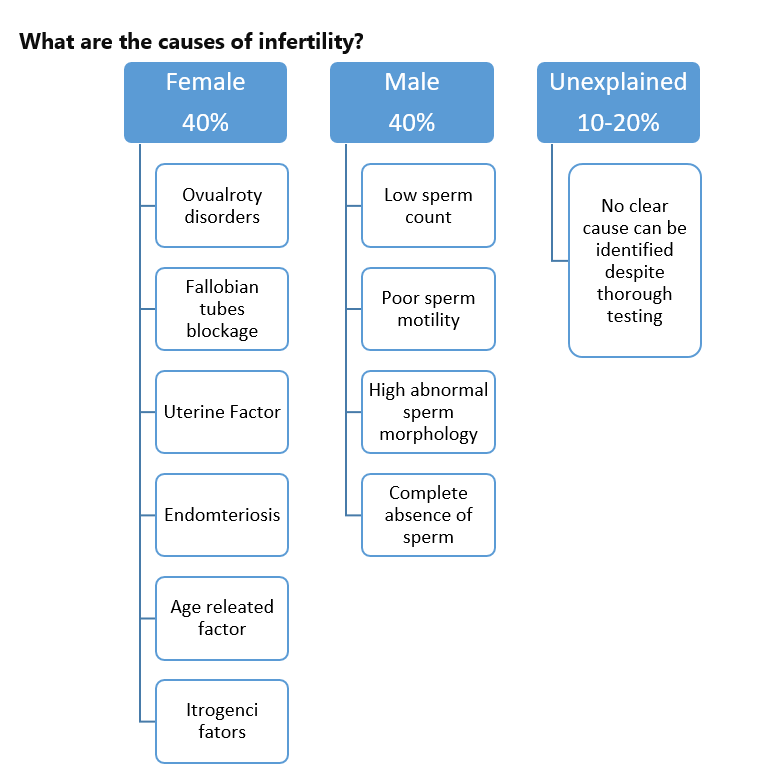
In females, it includes:
- Amenorrhea or menstrual irregularities
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Endometriosis
- Repeated abortions
- Painful menstruation
- Pelvic inflammatory diseases
- Previous history of cancer treatment
In males, it includes:
- Previous testicular trauma
- Inguinal or femoral hernia repair
- undescended testicles
- Previous history of cancer treatment
Are there any risk factors that can impact infertility for both couples?
- Advance age for both couples
- Weight-related issues (obesity or underweight)
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Substance abuse (Marijuana)
- Stress
There are more specific risk factors for males; like
- Anabolic steroid use
- Frequent exposure of the testicles to high temperatures (e.g. hot tubs, saunas, prolonged sitting)
- Exposure to environmental toxins including pesticides, lead, cadmium, or mercury
What are the types of infertility?
Primary Infertility: occurs when a couple has had no previous pregnancies before.
Secondary infertility: occurs when a couple has had a previous pregnancy before, whether successful or not, but struggles to conceive again. This could be due to changes in fertility factors since the previous pregnancy, such as age-related decline or new health issues.
What are the causes of infertility?
In some cases, it can be combined with male and female factors.
How to assess for infertility?
Medical Evaluation:
A comprehensive medical evaluation by a fertility specialist is crucial for diagnosing infertility. This includes a full detailed history, physical exams, hormone testing, imaging tests, and male partner workup.
What are the tests required for females with infertility?
- Ovulation testing: a blood test to check ovulation status in a woman.
- Ovarian reserve testing: a blood test to determine the type and dose of medication needed to enhance ovulation.
- Other hormonal testing: thyroid and prolactin hormones can also affect fertility.
- Pelvic ultrasound: to check the uterus, ovaries, and the eggs reserve.
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) to assess for fallopian tube blockages. It is an X-ray imaging test that is usually done after the injection of a dye into the uterus.
- Genetic Testing: In some specific cases.
What are the tests required for males with infertility?
Male workup is usually done with the cooperation of a specialist andrologist.
- Semen analysis: for all cases with infertility. A sperm sample is collected to check count, motility, and normal morphology parameters.
- Hormonal testing: a blood test to check for pituitary hormones and testosterones if needed.
- Scrotal ultrasound: in some cases, to check for varicocele or other abnormalities.
- Genetic testing: in some specific cases.
- Testicular biopsy: in specific cases after evaluation by the andrologist, a diagnostic or therapeutic biopsy might be scheduled according to the case.
What are the different kinds of treatment available for infertility?
- Accessing reputable fertility clinics and specialists: to ensure individuals receive personalized, evidence-based care tailored to their needs.
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle in all patients can positively impact fertility. This may include maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Ovulation induction: this can be done by fertility medications to regulate and induce ovulation in a woman, and it is considered the first treatment after proper evaluation in simple cases with patent both fallopian tubes.
- Surgery: Surgical procedures may be recommended to correct anatomical issues, remove blockages, or treat conditions such as endometriosis or fibroids.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): includes procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and intrauterine insemination (IUI).
- IUI is a fertility treatment where sperm is directly placed into a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization. It's often used with fertility medications to enhance ovulation and increase chances of success.
- IVF or ICSI is a fertility treatment where a single sperm is injected directly into a mature egg to assist with fertilization. It’s often used with fertility medications to grow more eggs to be collected. ICSI can also help the family to convince a healthy fetus if they have a certain gene mutation.
- Support and Resources: infertility can take an emotional toll, and seeking support from counselors or joining support groups can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies.
What are the options available for fertility preservation in our community?
Fertility preservation refers to methods used to retain reproductive potential for individuals who may want to have children in the future. Here are some common options:
- Egg freezing (oocyte cryopreservation): Women can undergo a procedure where their eggs are retrieved, frozen, and stored for later use. This can be beneficial for women who wish to delay childbearing due to personal or medical reasons, such as cancer treatment.
- Embryo freezing: Couples undergoing IVF can have their embryos frozen and stored for future use. This is often done when excess embryos are created during an IVF cycle, when there are concerns about the quality of the eggs or sperm, or if one of the couples might go under treatment that affects their fertility potential.
- Sperm freezing (sperm cryopreservation): Men can provide a sperm sample that is frozen and stored for later use. This is commonly done before undergoing cancer treatments that may affect fertility or for individuals in certain situations that pose a risk to fertility.
- Gonadal shielding: in cases where radiation therapy may affect fertility, gonadal shielding can be used to protect the reproductive organs from radiation exposure.
- Hormonal suppression: in some cases, hormonal medications can be used to suppress ovarian function temporarily, which may help preserve fertility during cancer treatment.
What is sex selection?
Also known as "family balancing", is a technique used to choose the sex of a baby before conception. There are generally two methods:
- Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS): it involves testing embryos created through IVF for genetic abnormalities as well as determining their sex. This technique allows parents to select embryos of the desired sex for transfer into the uterus. Medically, it can be used when there is a risk of passing on genetic disorders that are linked to a specific sex.
- Sperm Sorting: This method involves separating sperm into X-bearing (female) and Y-bearing (male) sperm using a specific technique. The desired sperm is then placed inside the uterus or used to fertilize the egg through IVF.
Get the Right Care for you & Your Family
(Saturday – Thursday from 08:00 AM to 10:00 PM)